When to See A Doctor For a Bee Sting
Animal & Bug Bites
•
Apr 18, 2022
Reviewed by:
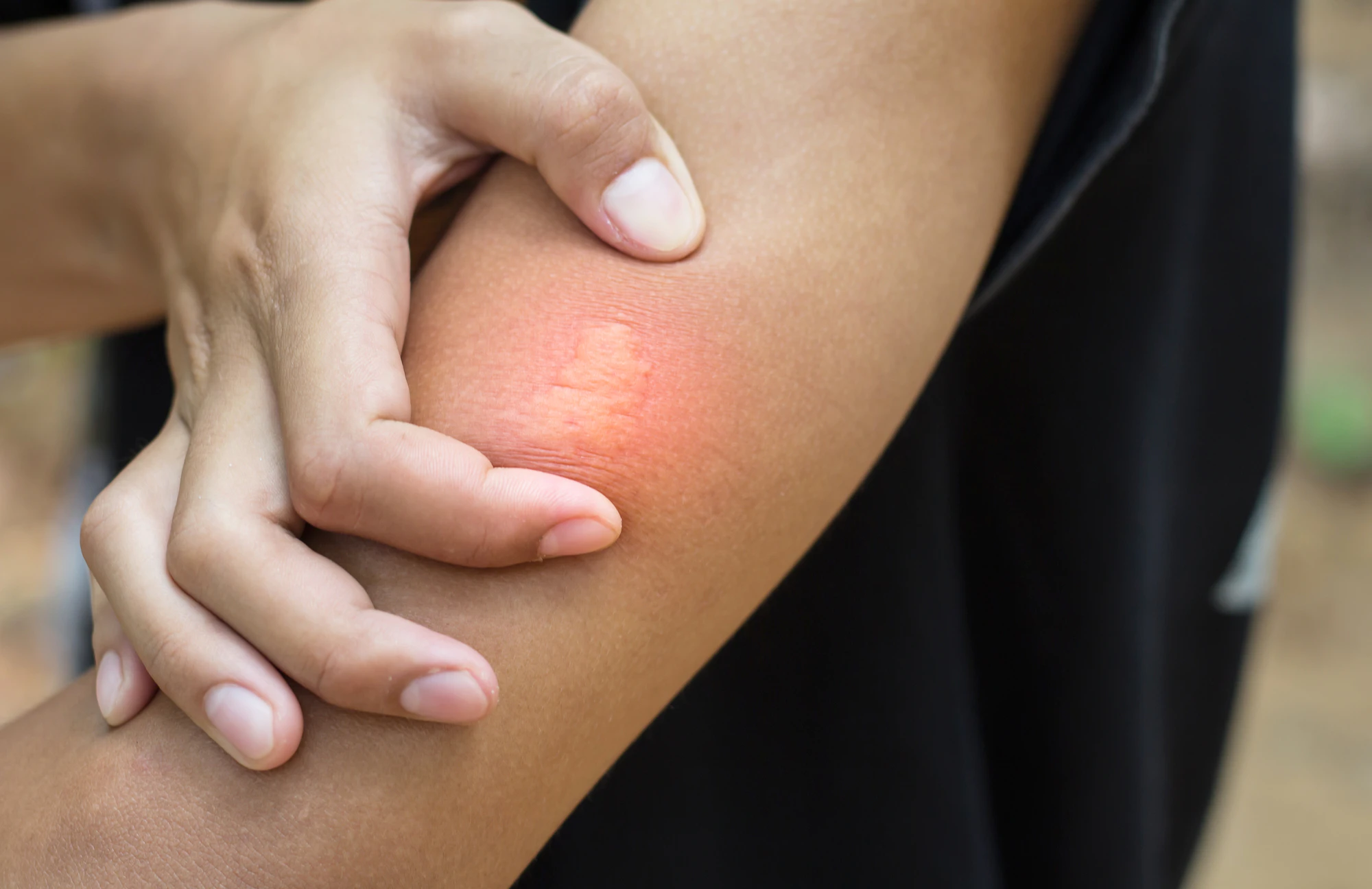
Wondering when to see a doctor for a bee sting? For most individuals, a bee sting doesn’t necessarily mean a trip to the hospital. Though in more severe cases, like for a small percentage of individuals who are allergic to bees or for individuals who suffer multiple bee stings, being stung can be life-threatening and may require an urgent trip to the emergency room.
If you’ve been stung by a bee or multiple bees, seek out bee sting emergency treatment if you notice symptoms such as hives, itching, trouble breathing or swallowing, swelling of the area, throat, or tongue, faintness, or nausea.
When should I be concerned about a bee sting?
When a bee stings you, it releases a venom that interacts with our immune systems and causes sharp pain and swelling around the sting area. Reactions to a bee sting range from mild symptoms that go away quickly to severe allergic reactions that require emergency medical treatment and/or the use of an EpiPen.
Mild bee sting reaction
In most cases, bee stings come with a quick, sharp pain, minor swelling, and a red bump where the bee stung you. Generally, the pain will subside within a few hours and will not require medical attention.
Moderate bee sting reaction
Moderate allergic reaction to bug bites or stings include symptoms such as:
- Extreme redness
- Swelling at the sting site
On their own, these symptoms are nothing to be concerned about and should resolve themselves with time. However, if they progress, the swelling spreads beyond the sting site, or your symptoms last longer than 10 days, you should call your doctor.
Severe bee sting reaction
If you’re wondering when to see a doctor for a bee sting and are experiencing a severe reaction to a bee sting, you need to head into the emergency room as soon as possible.
The reaction to a bee sting should be localized to the area where the sting occurred. If the reaction starts spreading, it’s time to seek bee sting emergency treatment, particularly if you have a known allergy to bees or are suffering from multiple bee stings.
Other severe allergic reaction symptoms to watch for include:
- Skin irritation such as hives, itching, and/or flushed or pale skin
- Trouble breathing or swallowing
- Severe swelling of limbs
- Swelling of your throat or tongue
- Loss of consciousness
- Vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain, and nausea
- Racing heartbeat
If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, do not wait to call 911 or head into the emergency room.
Severe allergic reactions to bee stings can cause anaphylactic shock — a potentially life-threatening emergency if not treated immediately. If you have a known allergy to bees and have been stung, use your prescribed emergency epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) as directed by your medical care provider.
How to treat a bee sting
Bee sting reactions and treatment will depend on the severity of the reaction, known allergies to bees, previous severe allergic reactions to bee stings, and whether you suffered multiple stings.
Mild to moderate bee sting reactions can be treated by:
- Check that the bee’s stinger and venom sack was not left inside your skin. If it was, you can scrape it away using your fingernail or pluck it out with tweezers. The important thing is to make sure you get it out fast, you can even use a credit card or a key to scrape it out.
- Wash the area with soap and water.
- Use an ice pack to stop the swelling. If you notice the bee sting swelling getting worse or the swelling spreads beyond the initial sting site, call for emergency help as you could be suffering from an allergic reaction.
If you are experiencing a severe bee sting reaction, outside of using an EpiPen, do not try to treat your symptoms at home. The emergency room will have all of the equipment and training necessary to intervene if your airways begin to close.
What happens if a bee sting goes untreated?
For those suffering from mild to moderate symptoms, leaving the bee’s stinger in your skin would be considered leaving your bee sting untreated. If the bee’s stinger is not removed it will continue to release venom into your bloodstream and can cause symptoms such as increased swelling, dizziness, difficulty breathing, and nausea. It also increases your risk of developing an infection at the sting site.
But for individuals who develop a severe allergic reaction, leaving severe symptoms untreated can lead to anaphylactic shock which can be life-threatening if it is not attended to quickly.
Head into a Complete Care ER for bee sting emergency treatment.
To know when to see a doctor for a bee sting, watch for symptoms such as hives, flushed or pale skin, difficulty breathing, swelling of your limbs, throat, or tongue, fainting, rapid pulse, or nausea.
If you notice any of these symptoms, do not wait to seek emergency care from a Complete Care freestanding, 24/7 emergency room. Prolonging treatment can cause a severe allergic reaction that could potentially be life-threatening.
With ER locations throughout Texas (Austin, Corpus Christi, San Antonio, Dallas/Fort Worth, East Texas, and Lubbock) and Colorado (Colorado Springs), we are fully equipped to take complete care of your medical emergency from diagnosis to treatment.
More Helpful Articles by Complete Care:
