Common Signs of an Allergic Reaction
Allergic Reactions
•
Jul 20, 2024
Reviewed by:
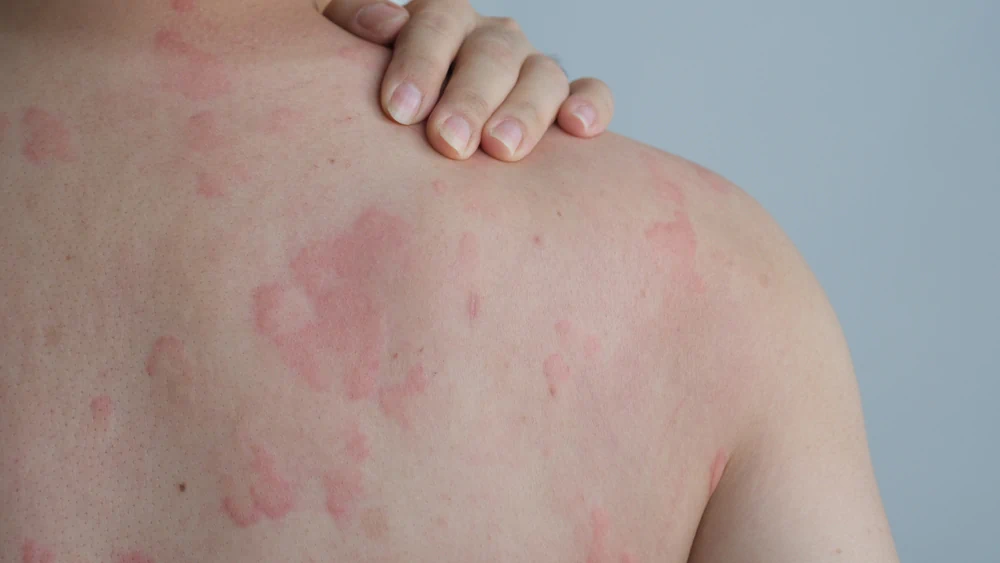
Suffering from allergies is a very common condition, even more common than you might think. In the United States, nearly 1 in 3 adults and more than 1 in 4 children suffer from some type of allergy. In fact, many patients who come into our emergency rooms seek treatment for an allergic reaction.
An allergic reaction occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens, which consist of typically harmless substances like pollen, bee stings, food, or pet dander. While allergic reactions are often not dangerous at all, in extreme cases, they can be deadly. Identifying the symptoms early can be crucial in managing and treating allergic reactions effectively and knowing when to seek emergency care.
Common signs of an allergic reaction include:
- Sneezing, runny, or blocked nose
- Itchy, red, and watery eyes
- Wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing
- Rashes or hives on the skin
- Swelling, particularly around the eyes, lips, tongue, or throat
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
- Anaphylaxis: a severe, potentially life-threatening reaction
Let’s discuss the signs and symptoms of an allergic reaction, their triggers, and when you may need to go to the emergency room to treat a reaction. If you think you may need emergency medical care, do not hesitate. Go to your nearest Complete Care ER location to be seen as quickly as possible.
What are the four types of allergic reactions?
When your immune system becomes overly sensitive to certain substances, known as allergens, it can lead to an adverse reaction. These reactions can present in a number of ways, and symptoms of allergies can range in severity depending on the type of allergic reaction and the allergen itself. However, there are four main types of allergic reactions to note.
- Anaphylactic (Type I): With Type I reactions, the symptoms will appear almost immediately after being exposed to pollen, dust, animal dander, or food. These reactions can range from your run-of-the-mill daily allergies to extreme allergic reactions such as anaphylactic shock.
- Cytotoxic (Type II): Unlike Type I, these symptoms appear within minutes to hours of contact with the allergen. Your immune system creates antibodies that damage cells by activating the “complement system” to fight off the allergen in your body, leading to inflammation. This cell damage can lead to conditions including anemia (lack of red blood cells) and Graves’ disease (the overproduction of thyroid hormones).
- Immunocomplex (Type III): These symptoms appear after several hours. The antibodies react with the allergens to form immune complexes. This is common in diseases like lupus, an autoimmune disease in which the person’s immune system attacks vital cells and organs, disrupting function. Symptoms can include high fever, abdominal or chest pain, and swelling in the limbs. Medical care should be sought out if these symptoms appear.
- Cell-mediated (Type IV): Also known as “delayed hypersensitivity,” these symptoms don’t appear until hours or days after the exposure and are usually associated with bacterial diseases.
How long can an allergic reaction last?
The answer to this question will depend on the type of allergic reaction you are experiencing. Generally, Type I reactions can last anywhere from a few minutes to several hours, while Type II and III reactions may persist for days. The symptoms associated with Type IV reactions can last for weeks or even longer.
What are early warning signs of an allergic reaction starting?
Recognizing the early warning signs of allergic reaction symptoms can help in seeking prompt medical attention to prevent further complications.
Itching and hives
Itching and hives occur because allergens stimulate the release of histamine from mast cells in the skin, leading to inflammation and irritation.
If you notice red bumps or irritation in patches on your skin, antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can alleviate the discomfort. It is also important to identify and avoid the allergen that triggered the reaction, if possible.
Swelling (angioedema)
Angioedema is swelling that typically occurs around the eyes, lips, hands, feet, and throat. It occurs due to the body’s release of histamine, which increases the permeability of blood vessels, allowing fluids to leak into surrounding tissues.
Over-the-counter antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine (in severe cases) can reduce swelling. However, if swelling affects breathing or swallowing, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Sneezing and nasal congestion
These symptoms are often the body’s reaction to inhaled allergens like pollen, dust, or animal dander. When the immune system detects proteins in these allergens, it releases chemicals such as histamines, which cause the nasal passages to become inflamed.
Decongestants and nasal corticosteroids can help relieve these symptoms. Avoiding known triggers and using air purifiers can also reduce the symptoms.
Shortness of breath and wheezing
Shortness of breath and wheezing indicate that an allergic reaction is affecting the respiratory system. This occurs when allergens cause the airways to constrict and produce excess mucus.
Individuals experiencing these symptoms should use prescribed bronchodilators or inhaled corticosteroids. In severe cases, an epinephrine injection may be necessary, and you should seek immediate medical assistance.
Gastrointestinal issues
Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can signal an allergic reaction to food allergens. These symptoms result from the immune system attacking the gastrointestinal tract.
If these symptoms occur, an antihistamine or corticosteroid prescribed by a doctor can help. Avoiding the triggering foods—no matter how much you enjoy them—and reading food labels carefully can prevent future incidents.
Learn more about how to treat lactose intolerance symptoms
When to go to the ER for severe allergic reaction symptoms
If you experience severe allergic reaction symptoms, it is essential to seek emergency treatment for allergies immediately.
Here are signs of when to go to the ER for an allergic reaction:
- Swelling of the lips or tongue that indicates throat closure
- Shortness of breath
- Severe skin rashes
- Dizziness or fainting
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Painful cramps
If you or a loved one have any of these more severe symptoms, it’s time to get them emergency care. Using an epinephrine auto-injector, if you have one, can offer temporary relief but shouldn’t replace seeing a doctor. Quick action is crucial because severe allergic reactions, called anaphylaxis, can become dangerous extremely fast.
Make sure to tell healthcare providers which allergen you suspect caused the reaction and any medications you’ve taken.
Need to go to the ER for an allergic reaction? Visit a Complete Care emergency facility.
Complete Care emergency facilities are equipped to handle a wide range of medical emergencies, including severe signs of an allergic reaction, allergic reactions in a baby, allergic reactions to bug bites, and more.
Our team of experienced healthcare professionals is trained in the rapid assessment and treatment of anaphylaxis, meaning patients can receive timely, accurate, and effective care. Additionally, each of our facilities is stocked with all necessary medications and equipment to manage critical conditions, including epinephrine, antihistamines, and corticosteroids.
With locations throughout Texas (Austin, Corpus Christi, Dallas/Fort Worth, East Texas, Lubbock, and San Antonio) and in Colorado Springs, we are dedicated to providing compassionate and comprehensive emergency care whenever and wherever you need it.
More Helpful Articles by Complete Care:
